Coupling Introduction
Sketch:
Coupling is a mechanical component used to firmly join the drive shaft and the driven shaft in different mechanisms to rotate together and transmit motion and torque.Sometimes it is also used to connect shafts to other parts (such as gears, pulley, etc.).It is often composed of two halves, respectively connected by a key or a tight fit, fastened at the end of the two axes, and then the two halves are connected in some way.The coupling can compensate the offset (including axial deviation, radial deviation, angular deviation or comprehensive deviation) between the two axes due to inaccurate manufacturing installation, deformation or thermal expansion during operation;As well as cushioning shock and absorbing vibration.
Most of the commonly used couplings have been standardized or normalized, and in general, only the correct choice of the type of coupling is required to determine the model and size of the coupling.If necessary, the load capacity of the vulnerable weak link can be checked and calculated;When the speed is high, it is also necessary to check the centrifugal force on the outer edge and the deformation of the elastic element, and carry out balance check.

Types:
Couplings can be divided into rigid couplings and flexible couplings two categories.
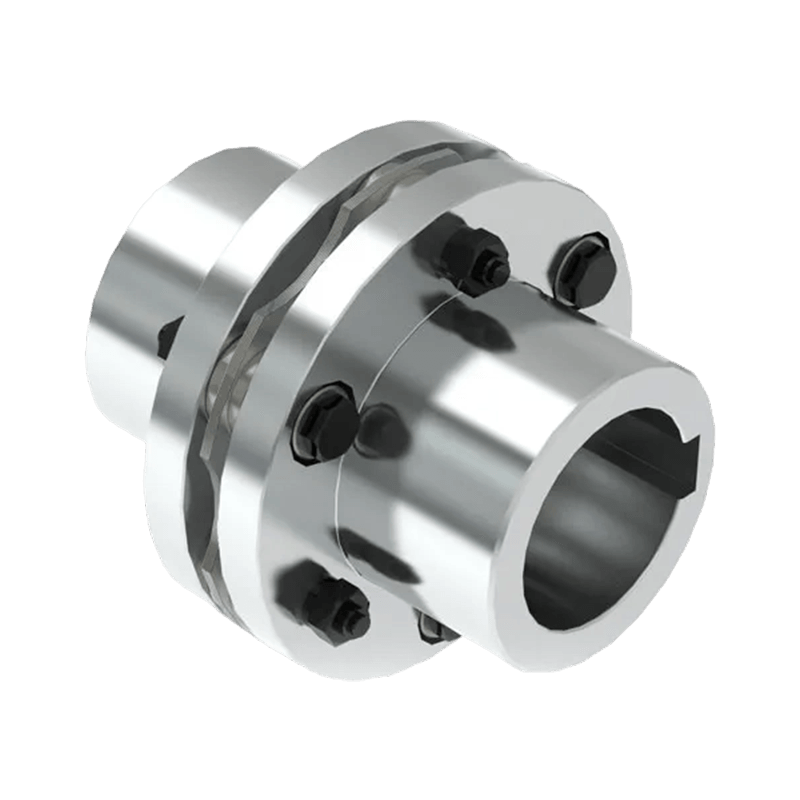
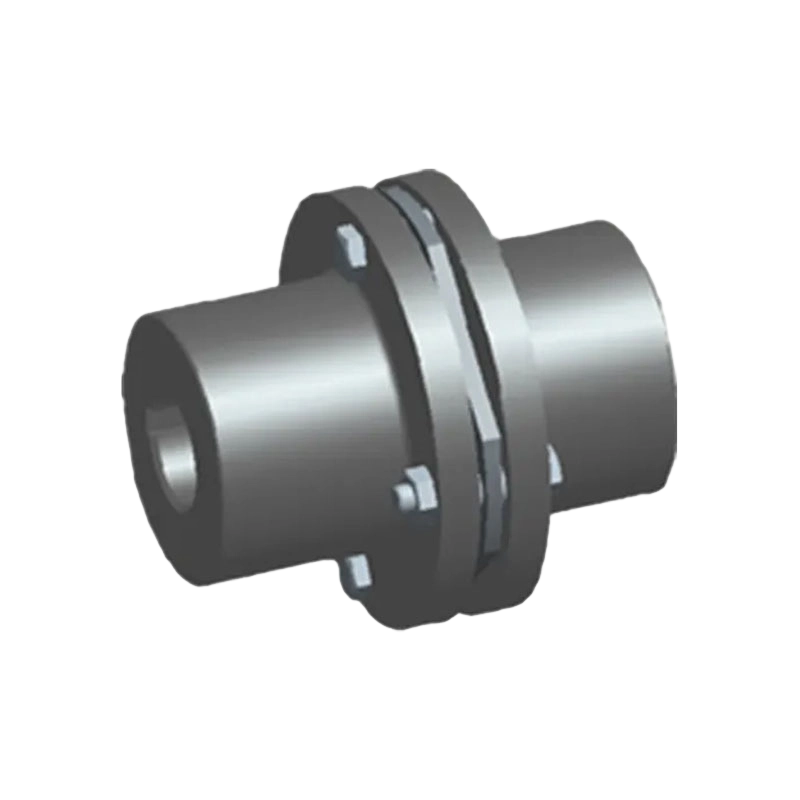
Rigid coupling does not have the ability to buffer and compensate the relative displacement of the two axes, requiring the two axes to be strictly aligned, but this kind of coupling has a simple structure, low manufacturing cost, easy installation and disassembly, and easy maintenance, which can ensure that the two axes have a higher neutral, larger transmission torque, and is widely used.Commonly used flange coupling, sleeve coupling and clamp coupling.
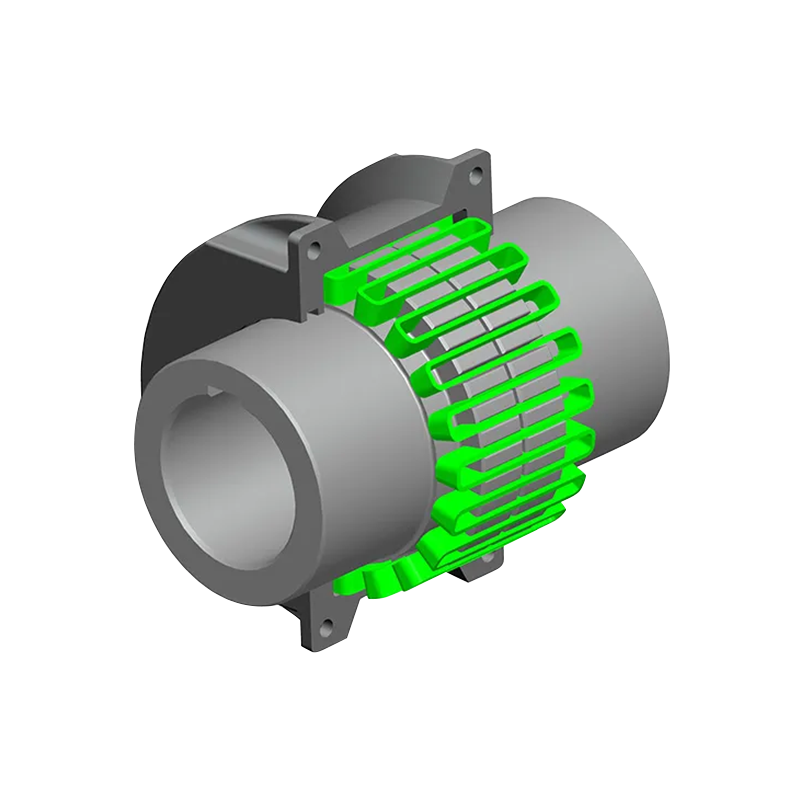
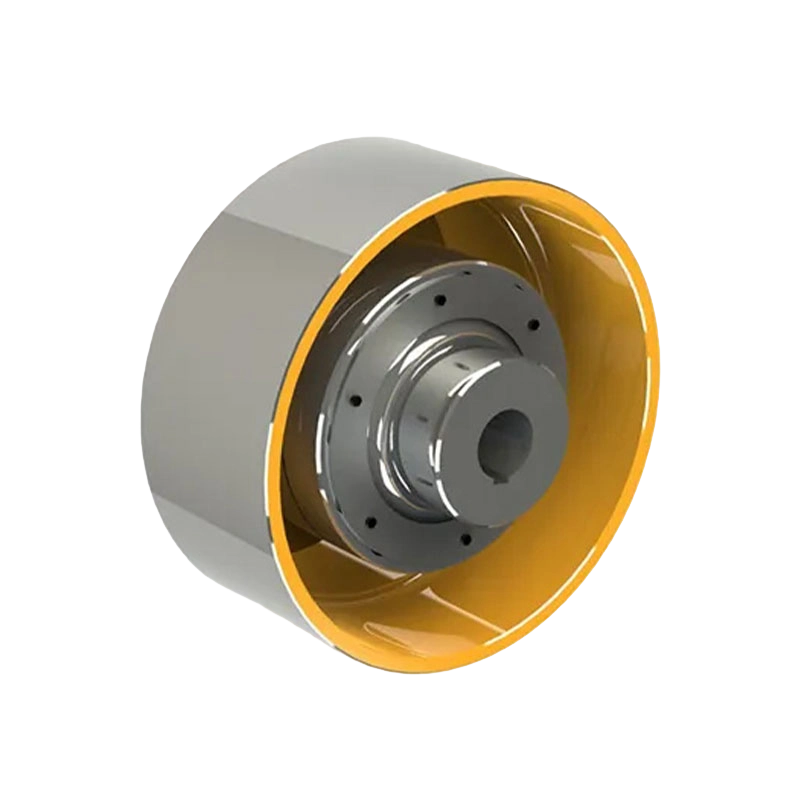
Flexible couplings can also be divided into non-elastic flexible coupling and flexible coupling with elastic components, the former type only has the ability to compensate the relative displacement of two axes, but can not buffer vibration reduction, common slider coupling, gear coupling, universal coupling and chain coupling;The latter type contains elastic components, in addition to the ability to compensate the relative displacement of the two axes, it also has a buffer and damping effect, but the transmitted torque is limited by the strength of the elastic components, generally less than the flexible coupling of inelastic components.Common with elastic sleeve pin coupling, elastic pin coupling, plum coupling, tire coupling, snake spring coupling and spring coupling.
Performance requirement:
According to different working conditions, the coupling should have the following performance:
(1) Mobility.The movability of a coupling is the ability to compensate the relative displacement of two rotating members.Factors such as manufacturing and installation errors between connected components, temperature changes during operation and deformation under load all require portability.Portability compensates for or relieves additional loads between shafts, bearings, couplings and other components due to relative displacement between rotating members.
(2) buffering.For the occasions of regular load starting or working load changes, the coupling needs to have a buffer and a damping elastic element to protect the prime mover and the working machine from less or no damage.
(3) Safe, reliable, with sufficient strength and service life.
(4) Simple structure, easy installation and maintenance.

Selection:
Coupling type selection When choosing a coupling type, the following items should be considered.① The size and nature of the required transmission torque, the requirements for buffering and vibration reduction functions, and whether resonance is possible.The relative displacement of the two axes is caused by manufacturing and assembly errors, shaft loading and thermal expansion deformation, and relative motion between components.(3) Allowable dimensions and installation methods, in order to facilitate assembly, adjustment and maintenance of the necessary operating space.For large couplings, it should be possible to achieve disassembly without axial movement of the shaft.



 English
English